Artificial intelligence is no longer a future concept—it is already shaping how we work, communicate, shop, and make decisions. From recommendation engines and virtual assistants to predictive analytics and automated decision systems, AI influences everyday life in ways many people don’t even notice. As AI becomes more powerful and deeply integrated into society, the importance of ethics in AI has never been greater.
Responsible artificial intelligence is not just a technical concern. It is a social, economic, and moral responsibility that affects individuals, businesses, and entire communities. Understanding why AI ethics matters is essential for building systems that are trustworthy, fair, and beneficial to everyone.
What Does Ethics in AI Really Mean?

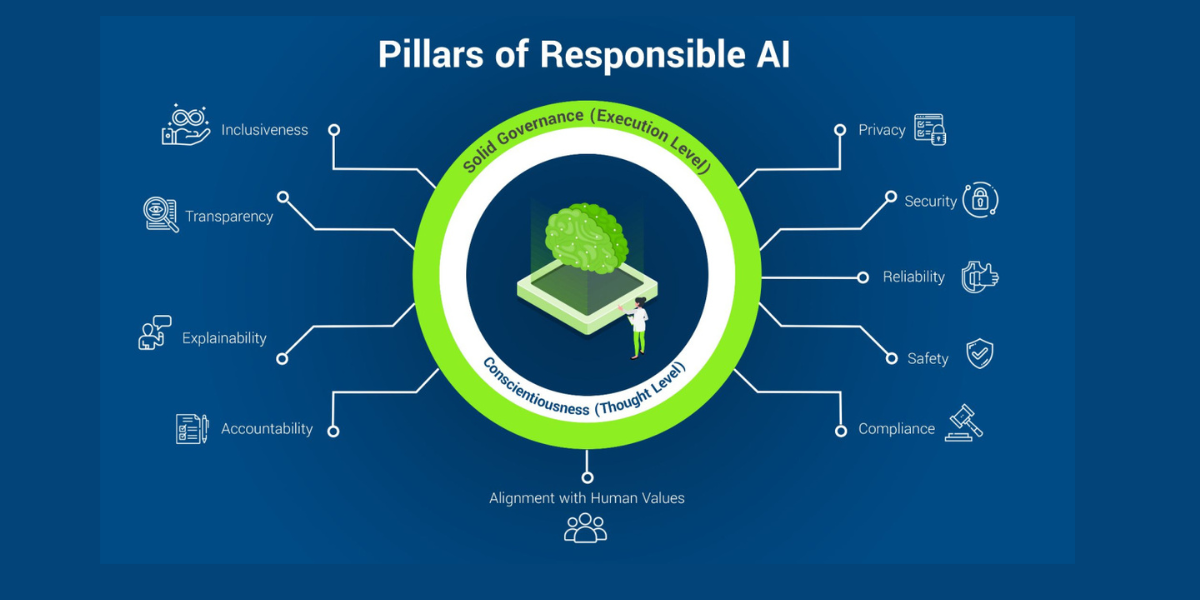
Ethics in AI refers to the principles and practices that guide how artificial intelligence systems are designed, trained, deployed, and monitored. Ethical AI aims to ensure that these systems act in ways that align with human values, respect rights, and minimize harm.
This includes addressing issues such as fairness, transparency, accountability, data privacy, and human oversight. Ethical AI is not about limiting innovation—it is about shaping innovation responsibly so that progress does not come at the cost of trust or social well-being.
The Growing Impact of AI on Decision-Making

AI systems are increasingly used to support or automate decisions in areas like finance, healthcare, recruitment, marketing, and law enforcement. While this can improve efficiency and accuracy, it also raises serious ethical concerns.
When AI systems make decisions based on biased or incomplete data, the outcomes can unfairly disadvantage certain groups. Without proper oversight, automated systems may reinforce existing inequalities rather than eliminate them. Ethical AI ensures that technology supports better decision-making without sacrificing fairness or accountability.
Addressing Bias and Fairness in AI Systems
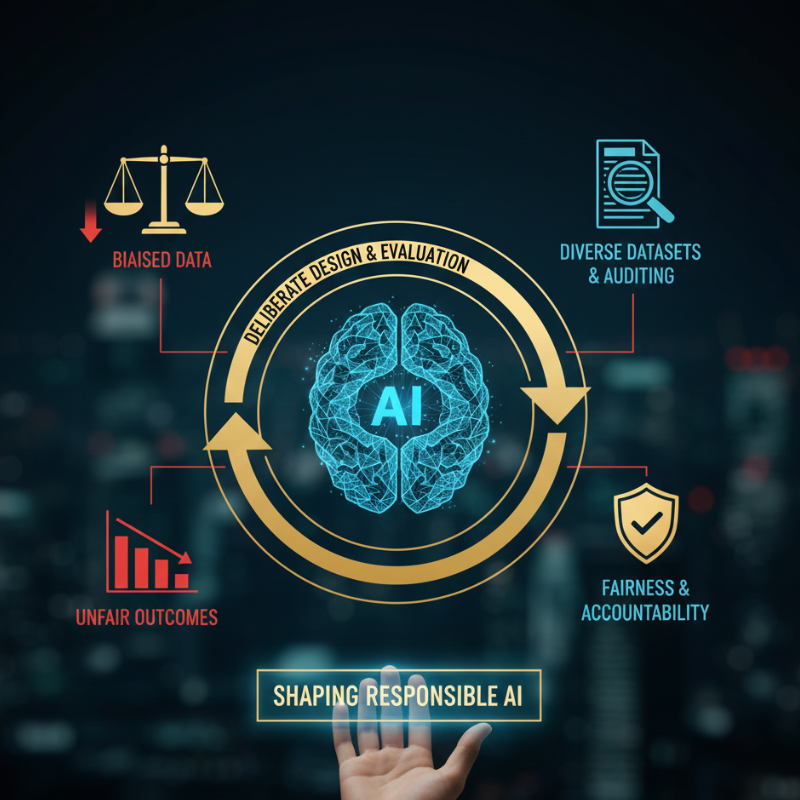
One of the most discussed ethical challenges in artificial intelligence is bias. AI systems learn from data, and if that data reflects historical or social biases, the AI can replicate and amplify them.
Responsible AI development involves identifying bias early, using diverse datasets, and regularly auditing systems for unfair outcomes. Fairness in AI does not happen by accident—it requires deliberate design choices and continuous evaluation. Ethical frameworks help organizations recognize and address bias before it causes real-world harm.
Transparency Builds Trust in Artificial Intelligence
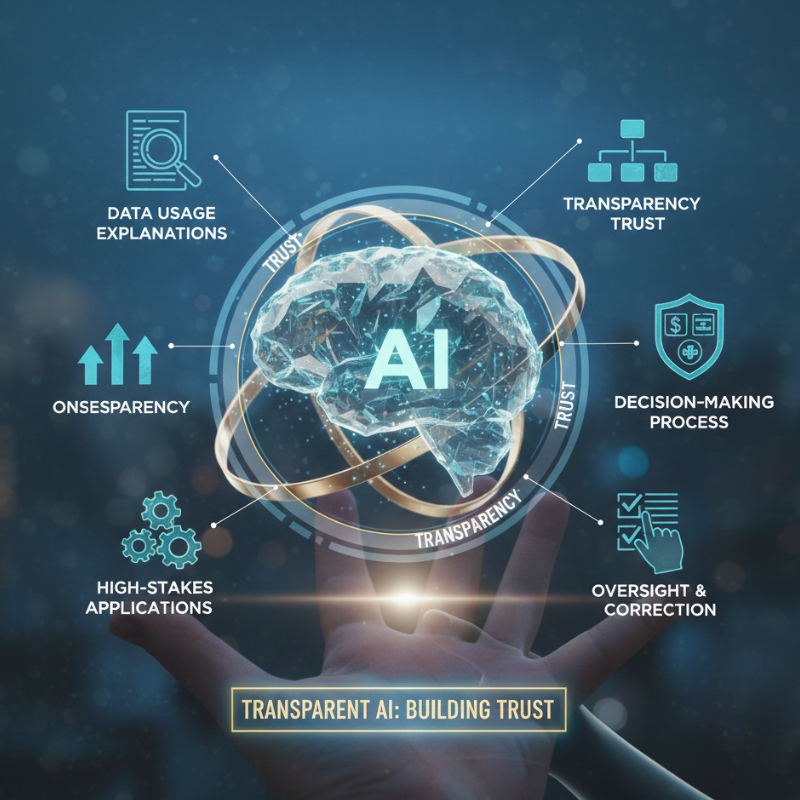
Transparency is a key pillar of ethical AI. Users should have a basic understanding of how AI systems influence decisions that affect them. When AI operates as a “black box,” trust erodes quickly.
Transparent AI systems provide clear explanations of how data is used and how decisions are made. This is especially important in high-stakes areas such as credit approval, medical diagnosis, or hiring processes. Transparency allows users, regulators, and organizations to question outcomes and correct errors when needed.
Data Privacy and Ethical AI Use

AI relies heavily on data, often personal and sensitive. Without strong ethical standards, data collection and usage can easily cross boundaries, leading to privacy violations and misuse.
Ethical AI prioritizes responsible data practices, including informed consent, data minimization, and secure storage. Respecting user privacy is not just a legal requirement—it is a fundamental aspect of building trustworthy AI systems. When users feel confident that their data is handled responsibly, they are more likely to accept and engage with AI-driven technologies.
The Role of Human Oversight and Accountability

No AI system should operate entirely without human oversight. Ethical AI recognizes that technology should support human judgment, not replace it completely. Clear accountability structures ensure that responsibility always lies with people, not algorithms.
When something goes wrong, organizations must be able to explain decisions, take corrective action, and accept responsibility. This human-centered approach ensures that AI remains a tool for empowerment rather than a source of unchecked authority.
Why Responsible AI Matters for Businesses

For businesses, ethical AI is not just a moral obligation—it is a strategic advantage. Organizations that prioritize responsible AI are better positioned to build long-term trust with customers, partners, and regulators.
Ethical practices reduce the risk of legal challenges, reputational damage, and public backlash. More importantly, they create sustainable innovation. Businesses that embed ethics into AI development are more likely to produce reliable, inclusive, and future-ready technologies.
Shaping the Future of Artificial Intelligence
As AI continues to evolve, ethical considerations must evolve with it. Governments, technology companies, researchers, and users all play a role in shaping how AI is developed and used. Ethical guidelines, industry standards, and open dialogue are essential for guiding progress in the right direction.
Responsible artificial intelligence is not about slowing down innovation—it is about ensuring that innovation benefits society as a whole. By prioritizing ethics, we can build AI systems that are not only intelligent but also fair, transparent, and worthy of trust.
Final Thoughts
Ethics in AI is no longer optional. As artificial intelligence becomes more influential, responsible development and deployment are essential for protecting individuals and strengthening public trust. Fairness, transparency, privacy, and accountability must remain at the core of every AI system.
If you’re interested in exploring more insights on artificial intelligence, data, and emerging technologies, keep learning how responsible innovation can shape a smarter and more ethical digital future.